A canonical tag tells search engines that a particular URL is the master copy of a page. Canonical tags are intended to avoid problems brought on by duplicate or identical material showing up on distinct URLs. Because this error message suggests that there are duplicate sites that have been correctly canonicalized, it is crucial to understand how to fix an alternate page with a canonical tag.
A canonical tag essentially tells search engines which version of a URL should show up in search results.
How to Fix Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag Status?
- Check for correctly canonicalized pages
- Check if the internal link structure needs assistance
- Check for issues with the crawl budget
Check for correctly canonicalized pages
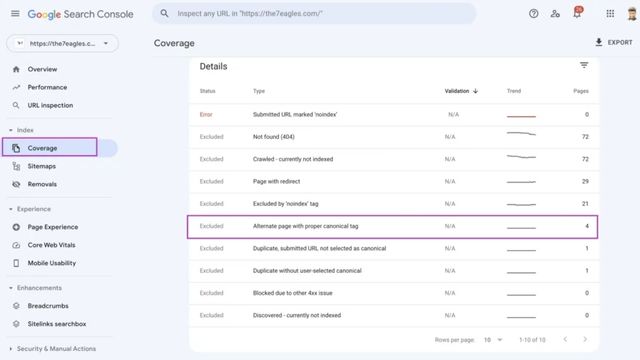
Check the pages listed under Coverage > Alternate page with valid canonical tags to see whether they need to be canonicalized. Update the canonical link to redirect to itself if these pages do not require canonicalization.
Check if the internal link structure needs assistance
Check the URL patterns of the pages if they have already been canonicalized correctly. Most likely, one would discover AMP pages, UTM-tagged URLs, and page versions. Although these are OK in most cases, they could become an issue in some situations.
Page variant overload
Sites with several page variations cause problems. There could be 25 URLs for each product, for instance, if an eCommerce site generates URLs for the same garment in all sizes and colors.
Making some pages invisible to search engines would be good because only a portion of URLs receives organic traffic. Including a # in the URL is one way to accomplish this.
Rogue UTM tags
If internal links in the sidebar, main navigation, body text, or footer are given UTM tags, things could go wrong. This undermines the transfer of page authority and should never be done. Even the data from Google Analytics is messed up.
Check for issues with the crawl budget
However, people do not influence how other people link to them. People can manage how they link to their information. One should keep an eye out for unfamiliar URLs when surfing sites with the status Alternate page with a suitable canonical tag.
One should think about utilizing a robots.txt file to prevent search engines from scanning URLs with the status Alternate page with a suitable canonical tag if a website only has a few thousand pages overall.
Saving money in this way helps the crawl. If a website has 10,000 pages or more, it is advised to consider crawl budget difficulties.
How to Apply a Canonical Tag?
The owner of the website should include a link tag at the top of the HTML code for the pages that Google should identify as canonical. For instance, the code must read as follows to mark http://www.xyz.com with the canonical tag: link rel=” canonical” href=”http://www.xyz.com” />
All pages that need to have a canonical tag can be given one by doing this. One can also use a content management system, such as WordPress, to streamline this work.
What Does “Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag” Mean?
When Google Search Console displays the status message “Alternate Page with Proper Canonical Tag,” it signifies that two different versions of the same page on your website share the same canonical URL. Simply excluding the duplicate copy, Google will only index the original version of the page.
In theory, this indicates that Google correctly recognizes these canonicalized URLs and that you are not required to take any further action.
Despite this, you should periodically review them to determine whether these pages should be canonicalized. If not, you risk losing the possible traffic from the worthwhile pages that might have been indexed.
What Is a Canonical Tag?
Search engines should index the version of a webpage designated as the “master” or “canonical” version, according to a canonical tag. It makes it easier for you to define the URL version you want to show up in search results. This is helpful since you can utilize canonical URLs to prevent duplicate content from adversely affecting rankings in specific situations where you may have material accessible via various URLs or different websites entirely.
Consider two pages on your website that are remarkably similar to one another.
- rankmath.com/page1
- rankmath.com/page2
Although the content of the two pages is similar, you want search engines to only index the canonical version of the page (in this case, rankmath.com/page1).
To accomplish this, you would add the following canonical tag to both the HTML code of rankmath.com/page1 and page2:
Link: “https://rankmath.com/page1”; canonical
Indicating that rankmath.com/page1 is the page’s canonical version and should be indexed, this informs search engines.
How do you resolve canonical issues?
Canonical problems can be fixed in one of two ways: by creating 301 redirects or by including a “canonical” tag on the pages of your website. What you’re seeking to solve will determine the best course of action.
How do I fix a missing canonical tag?
Choose which of the URLs with identical or similar content should be the canonical version first. Then, point the target to the preferred (canonical) URL by adding the rel=canonical tag to each page in the relevant group of URLs.
Can I change the canonical URL?
A blog post’s or page’s canonical URL can be manually added or changed. Your canonical URL settings will be superseded by canonical URLs created in this manner.
Is canonical link important?
In other words, the canonical URL element tells Google and other search engines what URL to index the content of a particular page under when they crawl a website. This is significant because different URLs may serve the same or very similar content, depending on several different circumstances.
Does every page need a canonical tag?
Don’t forget to add a canonical tag to every page. To avoid any potential repetition, a canonical tag should be present on every page (including the canonical page). A page should still have a canonical tag that links to itself even if there are no other versions of it.
- How To Block Websites On iPhone And iPad
- How to Fix Google Soft 404 Errors
- Google Chrome to Drop Support for Windows 7/8.1 in Feb 2023
Conclusion
Search engines can be instructed via a canonical tag which version of a URL should appear in search results. Canonical tags are used to prevent issues caused by identical or duplicate content appearing on different URLs. If these pages don’t need to be canonicalized, update the canonical link to point to themselves. People have control over how links to their information are made online. When browsing websites with the status Alternate page with an appropriate canonical tag, one should be on the lookout for unknown URLs.
It is advised to take crawl budget issues into account for websites with 10,000 or more pages. A canonical tag specifies which version of a webpage is the “master” or “canonical,” and that version should be indexed by search engines.