How to Fix Ubuntu Boot Problem
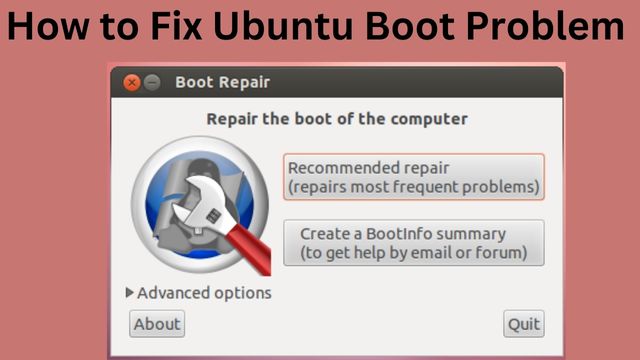
Though generally dependable, Ubuntu occasionally fails to boot. Here are a few typical reasons why Ubuntu won’t start, as well as solutions.
Your computer is turned on as you get ready to work, edit a document, create music, or simply play a game, but something goes wrong.
The Ubuntu Boot problem occurs.
Sadly, despite Ubuntu’s popularity and relative dependability, it occasionally has issues, just like Windows 10 or macOS. You can usually find a way to get around this.
Here’s what to do if Ubuntu won’t boot, whether you’re using an Ubuntu desktop or Ubuntu Server.
How to Fix Ubuntu Boot Problem
- Is the Grub Bootloader working?
- Check for Bootable devices
- Reinstall Ubuntu
- Repair the Bootloader menu
- Replace faulty hardware
Ubuntu usually functions right out of the box. Ubuntu may start very slowly or not, indicating a booting problem.
These procedures can be used with different Linux operating systems even though they are intended for Ubuntu users. However, remember that some of these workarounds won’t work if you’re using disc encryption.
It’s time to complete these five procedures if your Ubuntu system won’t boot. These can be used whenever regardless of how long you’ve been using Ubuntu or whether it’s not loading immediately after installation.
Is the Grub Bootloader working?
The bootloader, known as GRUB, makes sure the chosen operating system boots. It will list and start all installed operating systems, including Windows, on a dual-booting computer.
But installing Windows alongside Ubuntu may result in the bootloader being overwritten, which will make it difficult to start Ubuntu.
Other problems, such as a failed upgrade or a power outage, can damage the bootloader. You might notice an error saying something like “grub failed boot detection” in any circumstance.
- Restart your computer while holding Shift to check the GRUB bootloader.
- The list of installed operating systems should now appear; use the arrow keys to traverse the menu.
If not, the GRUB bootloader may be corrupted or the cause of the issue. The only fix is to repair the bootloader. (You will still be able to access Windows if you are dual booting.)
Repair the GRUB Bootloader to Boot Ubuntu
Ubuntu won’t start if GRUB doesn’t load. Fortunately, using the Ubuntu installation DVD, you can fix GRUB. With the disc still in place, restart the computer and wait for it to load.
Once more, you might need to alter the boot order as previously said. Before you modify the boot order, make a note of it!
Verify your network connection after the installation DVD has booted into the Live environment, and then open a Terminal. Enter:
- sudo grub-install /dev/sda
You can also grub with:
- sudo update-grub
Now that your computer has restarted, Ubuntu ought to start up. Alternatively, the GRUB bootloader menu will have a selection for it.
Check for Bootable device
If Ubuntu won’t start, there might be a bootable disc attached.
It’s not just you. One of the most frequent issues with Ubuntu not booting up typically happens shortly after installation.
This is due to the boot device being set to the Ubuntu boot disc (USB device or DVD). Because of this issue, the installer urges you to remove your installation media before starting your computer.
Boot into the system UEFI/BIOS or boot order menu to check the current boot device. The POST screen, which appears when your PC turns on, can be used to access both. Look through the computer’s (or motherboard’s) manual if you have difficulties locating the boot order option.
Reinstall Ubuntu
It might be preferable to just reinstall Ubuntu if there is a problem that could take a long time to fix. You may accomplish this without replacing your current files and folders. If Ubuntu won’t boot, it’s one of the simplest solutions.
- First, as previously mentioned, boot into the Live environment on your Ubuntu installation disc.
- Next, start installing Ubuntu.
- Choose Reinstall Ubuntu when the installer finds that Ubuntu is already installed.
- The choice that says “Documents, music, and other personal files shall be kept” should be chosen.
- Continue with the reinstallation
Of course, you ought to already have a backup of all of your Ubuntu data as a safety measure. This may have been done by hand using a backup program or a disc cloning program like dd.
After the reinstallation is finished, Ubuntu ought to be operational once more.
Not recommended unless all other alternatives have failed is the Erase Ubuntu and Install option. Once more, you should back up your data beforehand.
Repair the Bootloader menu
You don’t need to perform any of the aforementioned steps if you can see the bootloader. When Ubuntu won’t boot, there is a built-in recovery program that can help.
Located in the bootloader menu:
- Choose Ubuntu’s advanced options.
- The entry following is to be chosen by using the arrow keys (recovery mode).
- To continue, hit Enter.
Watch as a condensed version of the Ubuntu operating system boots up. You’ll see that this is comparable to Windows Safe Mode if you’ve ever booted in that mode.
When Ubuntu won’t boot, there are several fixes you can try. In sequence, these are the three you ought to try:
fsck:- This utility, known as the file system checker, analyses the hard drive and fixes any faults it discovers.
clean:-If a lack of HDD space is the cause of Ubuntu not booting, try this to create free space.
dpkg:- You can fix damaged software packages using this. Ubuntu startup issues might be brought on by unsuccessful software updates or installations. It should be possible to fix them.
Try the failsafe X utility as well if you recently installed Ubuntu and it won’t boot. In this case, the issue may be with the graphics drivers or the Xorg graphical server. To fix this Ubuntu booting error, use failsafe X.
Keep in mind that the root menu option is intended for experienced users who know to solve the issue manually.
Replace faulty hardware
Hardware problems are yet another reason why Ubuntu won’t boot. Boot issues may result from:
- A cabling or hard disc drive (HDD) issue
- Faulty motherboards
- A CPU (processor) issue
- Difficulties with power supply units (PSUs)
Unless you made a backup, you’ll normally have to reinstall Ubuntu after a bad HDD is replaced. Even though it’s a “scorched earth” strategy, this will fix Ubuntu’s starting-up issues.
Say Goodbye to Ubuntu Boot Loading Problems
Whether you recently installed Ubuntu or have been using it for some time, if it won’t boot, there may be a difficult repair.
It can take a while before your machine is usable again if the GRUB bootloader cannot be fixed. Another reason to have consistent backups, or at the very least sync your important data with the cloud!
Not only Ubuntu, but any operating system can experience this.
How do I fix the Ubuntu boot menu?
- A partition table backup
- A device’s boot sectors backup
- Set up the GRUB bootloader.
- Prepare the GRUB bootloader.
- Include kernel options
- The GRUB default OS can be modified.
- The MBR must be compatible with Windows.
- Rectify a faulty filesystem.
How do I force Ubuntu to boot?
To access the GNU GRUB menu in BIOS, swiftly press and hold the Shift key. (If the Ubuntu logo appears, you have missed the opportunity to access the GRUB menu.) Press the Escape key in UEFI (perhaps more than once) to access the grub menu.
Why my Ubuntu is not opening?
Holding the Shift key down while starting your PC. You have visited the GRUB boot loader if you see a menu containing a list of operating systems. Ubuntu may not launch if the GRUB boot loader has been overwritten and you don’t get a menu with a list of boot options.
Conclusion
If your Ubuntu computer won’t boot up, whether it be a desktop or a server, there are solutions available. Although these steps are aimed at Ubuntu users, they can also be utilized with other Linux operating systems. Some of these workarounds won’t function if you disable your disc encryption. You can resolve problems with the GRUB bootloader that prevents Ubuntu from booting using the installation DVD for Ubuntu.
The command sudo grub-install /dev/sda can also be used to install grub. alternatively, create a Terminal account and experiment with a different boot order. Here are some suggestions to help you if you recently installed Ubuntu and it won’t boot up or if you’ve been using it for a while and it’s having problems starting up.





🙏 🙏 ❤ ❤ Always be updated with computer tips, mobile tips, how to fix, tech reviews, and tech news on Rowdytech, or subscribe to the YouTube channel.